DelveInsight’s Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Market Insights, Epidemiology, and Market Forecast-2028’ report delivers an in-depth understanding of the catheter-related bloodstream infection, historical and forecasted epidemiology as well as the catheter-related bloodstream infection market trend in the United States, EU5 (Germany, Spain, Italy, France, and United Kingdom), Japan, APAC (China, India, Taiwan, South Korea, and Australia), LATAM (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia), Middle East (Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates), and Russia.
Geography Covered
• The United States
• EU5 (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom)
• Japan
• APAC (China, India, Taiwan, South Korea, and Australia)
• LATAM (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia)
• Middle East (Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates)
• Russia
Study Period: 2017–2028
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection: Disease Understanding and Treatment Algorithm
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Overview
Catheter-related bloodstream infection also known as catheter-related sepsis, defined as the presence of bacteremia originating from a catheter insertion. Antibiotics such as antibacterial and antifungal are used for the treatment of the disease. Antibiotic lock therapy is considered as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of CRBSI when catheter removal is not a favorable option. The current treatment options are used as off-label therapies and only a few non-antibiotic lock solutions are approved in Europe.
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Diagnosis
The diagnosis of catheter-related bloodstream infection remains a major challenge. Fever and chills that are often associated with catheter-related bloodstream infections are not specific. Furthermore, local catheter inflammation and phlebitis could exist in the absence of catheter-related bloodstream infection or even a local infection, as has been reported with peripherally inserted central catheters. The ‘gold standard’ for the diagnosis of catheter-related bloodstream infection is the combination of positive blood culture with the same organism isolated from the catheter. However, a major diagnostic problem is that traditional methods of catheter culture necessitate the removal of the central venous catheters (CVC), whereby the line tip is either rolled on an agar plate or placed in a nutrient broth.
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Treatment
It covers the details of conventional and current medical therapies available in the catheter-related bloodstream infection market for the treatment of the condition. It also provides the treatment guidelines and algorithms of the United States and Spain.
The DelveInsight’s catheter-related bloodstream infection market report gives a thorough understanding of catheter-related bloodstream infection by including details such as disease definition, causes, risk factors, pathogenesis, and diagnosis.
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Epidemiology
The disease epidemiology covered in the report provides historical as well as forecasted epidemiology segmented by Total Incident Population of Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Total Diagnosed Incident Population of Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection, and Diagnosed Incidence of Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection by Causative Pathogens scenario of catheter-related bloodstream infection in the global market covering the United States, EU5 countries (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and United Kingdom), Japan, APAC (China, India, Taiwan, South Korea, and Australia), LATAM (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia), Middle East (Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates), and Russia from 2017 to 2028.
Key Findings
This section provides glimpses of the catheter-related bloodstream infection epidemiology in the global market.
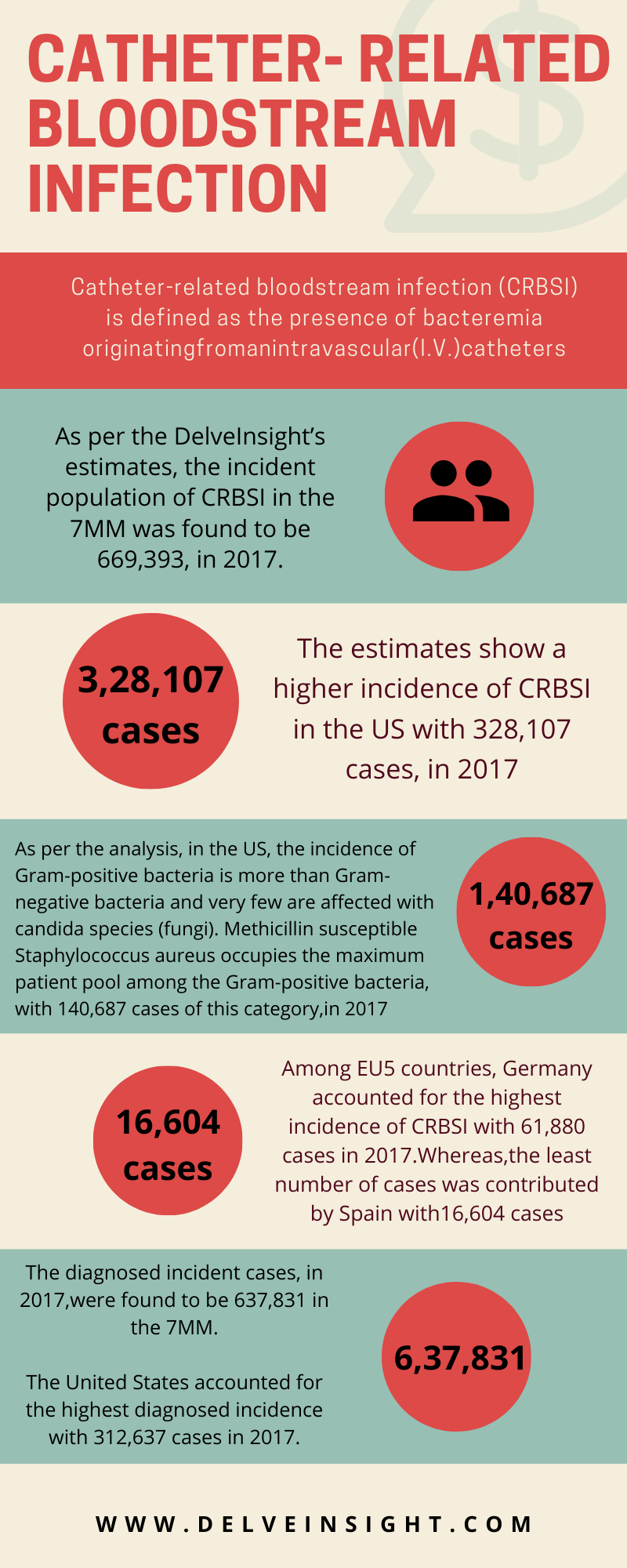
As per DelveInsight’s analysis, the total incident population of catheter-related bloodstream infection in the global market was found to be 4,114,882 in 2017. The estimates show a higher incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infection in India with 1,722,280 cases in 2017.
Country Wise- Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Epidemiology
The epidemiology segment also provides the catheter-related bloodstream infection epidemiology data and findings across the United States, EU5 (Germany, France, Italy, Spain, and the United Kingdom), Japan, APAC (China, India, Taiwan, South Korea, and Australia), LATAM (Brazil, Mexico, Argentina, and Colombia), Middle East (Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates), and Russia.
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Drug Chapters
The drug chapter segment of the catheter-related bloodstream infection report encloses the detailed analysis of catheter-related bloodstream infection marketed drugs and late stage (phase III) catheter-related bloodstream infection pipeline drugs. It also helps to understand the catheter-related bloodstream infection clinical trial details, expressive pharmacological action, agreements and collaborations, approval and patent details, advantages and disadvantages of each included drug and the latest news and press releases.
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Marketed Drugs
Neutrolin: CorMedix
Neutrolin (CRMD003), is a non-antibiotic, anti-infective developed by CorMedix as a preventative solution to decrease the threat of infection and blood clots (thrombosis), thereby keeping CVCs operating safely and efficiently. It is a catheter lock solution for the prevention of catheter-related bloodstream infection and maintenance of catheter patency in hemodialysis patients.
Taurosept: Geistlich Pharma
TauroSept is an antimicrobial solution (lock solution) developed by Geistlich Pharma for the prevention of catheter-related infection and is intended for installation in intravenous catheters between treatments to lock the catheter. It mainly contains antibacterial chemotherapeutic agent taurolidine.
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Off-label Drugs
Daptomycin
Daptomycin is a cyclic lipopeptide parenteral antibiotic derived from Streptomyces roseosporus. It exhibits rapid concentration-dependent bactericidal activity against Gram-positive pathogens such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Vancomycin is a tricyclic glycopeptide antibiotic originally derived from the organism Streptococcus orientalis. Vancomycin is used for the treatment and prevention of various bacterial infection caused by Gram-positive bacteria, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Catheter-Related Bloodstream Infection Emerging Drugs
Mino-Lok: Citius Pharmaceuticals
Mino-Lok is an antibiotic lock solution used to treat patients with central line-associated bloodstream infection/catheter-related bloodstream infection. It is a combination of minocycline, edetate (disodium EDTA), and ethyl alcohol, all of which act synergistically to break down bacterial biofilms, eradicate the bacteria, provide anti-clotting properties to maintain patency in CVCs, and salvage the indwelling catheter.
The catheter-related bloodstream infection market outlook of the report helps to build a detailed comprehension of the historic, current and forecasted catheter-related bloodstream infection market trends by analyzing the impact of current therapies on the market, unmet needs, drivers and barriers, and demand of better technology.
This segment gives a thorough detail of catheter-related bloodstream infection market trend of each marketed drug and late-stage pipeline therapy by evaluating their impact based on annual cost of therapy, inclusion and exclusion criteria’s, mechanism of action, compliance rate, growing need of the market, increasing patient pool, covered patient segment, expected launch year, competition with other therapies, brand value, their impact on the market and view of the key opinion leaders. The calculated market data are presented with relevant tables and graphs to give a clear view of the market at first sight.
According to DelveInsight, catheter-related bloodstream infection global market is expected to change in the study period 2017–2028
Comments
Post a Comment